Characteristics of Autism
Social
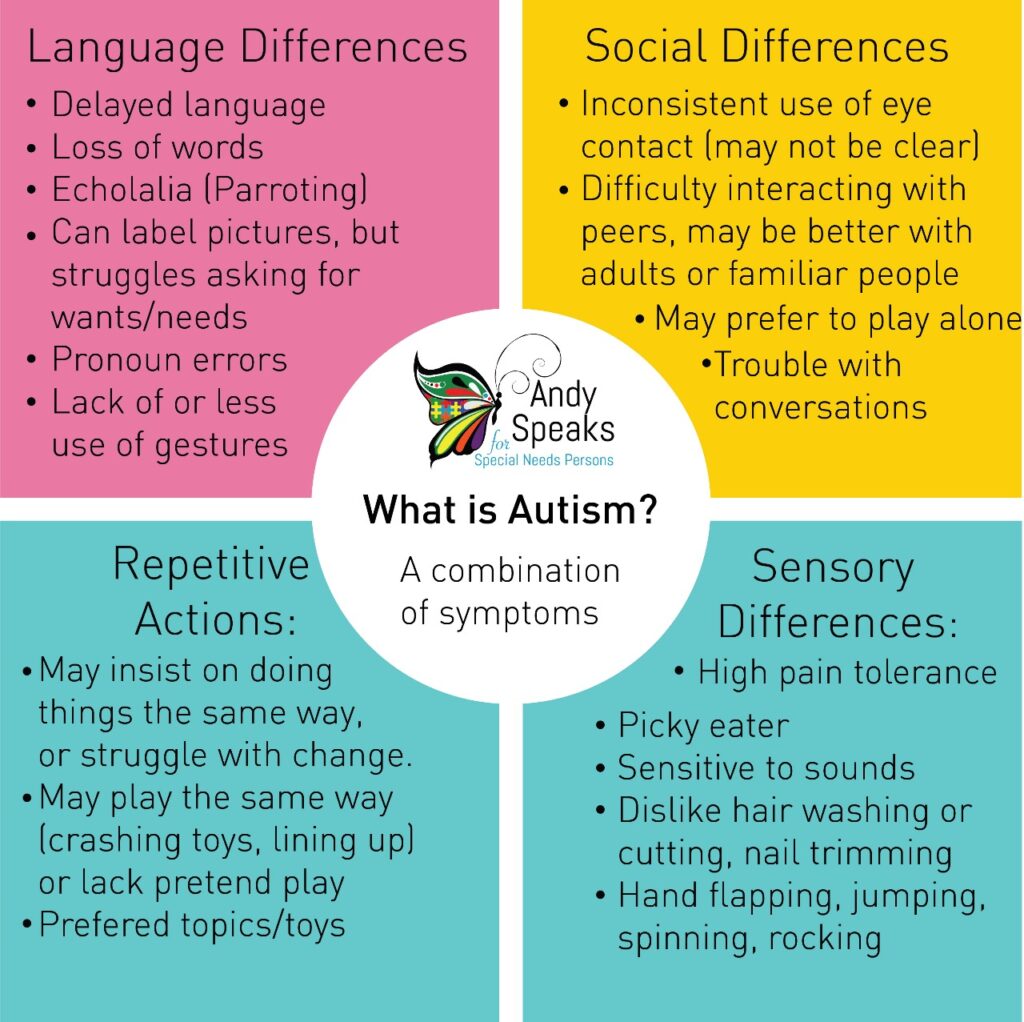
 Social interaction difficulties are a core feature of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Individuals with ASD may struggle with understanding social cues, developing and maintaining relationships, and communicating effectively with others. These difficulties can make it challenging for them to navigate social situations and form meaningful connections with others.
Social interaction difficulties are a core feature of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Individuals with ASD may struggle with understanding social cues, developing and maintaining relationships, and communicating effectively with others. These difficulties can make it challenging for them to navigate social situations and form meaningful connections with others.
Behavioral therapy, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) and social skills training, can be effective in improving social interaction skills in individuals with ASD. ABA therapy can help individuals learn new social skills, such as taking turns, initiating conversations, and reading social cues. Social skills training can provide opportunities for individuals to practice social skills in a safe and structured environment.
In addition to behavioral therapy, speech therapy can also be helpful in improving communication skills in individuals with ASD. Speech therapy can help improve language comprehension, speech production, and pragmatic language skills, which are the social rules for communication, such as taking turns, staying on topic, and using appropriate tone of voice.
It’s important to work with healthcare professionals who specialize in treating ASD to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets the unique needs of the individual.
 Eye contact is a behavior that involves looking at another person’s eyes during a conversation or social interaction. It is an important aspect of nonverbal communication, as it can convey emotions, intentions, and social cues.
Eye contact is a behavior that involves looking at another person’s eyes during a conversation or social interaction. It is an important aspect of nonverbal communication, as it can convey emotions, intentions, and social cues.
In autism spectrum disorder (ASD), eye contact may be limited or absent during social interactions. This can make it difficult for individuals with ASD to read social cues and interpret the emotions of others.
The reasons for limited eye contact in ASD are not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to the differences in the way individuals with ASD process social information. Some individuals with ASD may find it overwhelming to process both verbal and nonverbal information at the same time, leading them to avoid eye contact to reduce the sensory input.
However, it’s important to note that not all individuals with ASD have difficulty with eye contact. Some individuals with ASD may make eye contact, but have difficulty interpreting social cues or maintaining eye contact for extended periods of time.
Social skills training and therapy can be helpful in improving eye contact and other social communication skills in individuals with ASD. A therapist can work with the individual to develop strategies for making eye contact and interpreting social cues, and can help the individual to feel more comfortable in social situations.
Solo play is common among individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Many individuals with ASD may prefer to play alone, engage in repetitive or stereotyped play behaviors, or have narrow interests in specific toys or activities.
While solo play can be a source of comfort and enjoyment for individuals with ASD, it’s also important to encourage and support social play and interaction with peers. Social play can help individuals with ASD learn social skills, such as turn-taking, sharing, and communication, and can provide opportunities for them to practice these skills in a safe and supportive environment.
Social skills training and behavioral therapy, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), can be effective in improving social play skills in individuals with ASD. ABA therapy can help individuals learn new play skills, such as engaging in joint play, sharing toys, and following social rules for play. Social skills training can provide opportunities for individuals to practice social play skills in a structured and supportive environment.
Behavioral
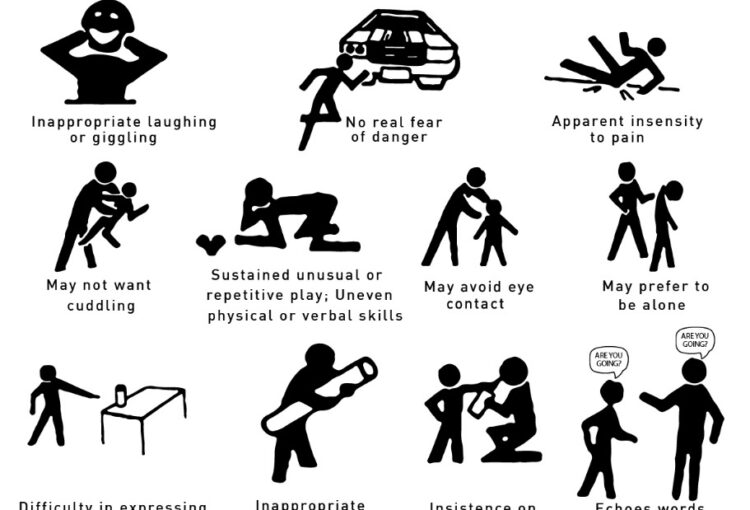
 Stimming, short for self-stimulatory behavior, refers to repetitive or stereotypical movements, sounds, or behaviors that are often seen in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or other developmental or neurological conditions.
Stimming, short for self-stimulatory behavior, refers to repetitive or stereotypical movements, sounds, or behaviors that are often seen in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or other developmental or neurological conditions.
Stimming behaviors can take many forms, such as hand flapping, rocking back and forth, spinning, humming or making repetitive vocal sounds, or staring at lights or objects. These behaviors can serve different purposes for individuals with ASD, such as self-soothing, self-regulation, or sensory seeking.
While stimming behaviors can be a way for individuals with ASD to cope with sensory overload or anxiety, they can also interfere with social interaction and communication. Speech and occupational therapy can be helpful in identifying and addressing the underlying sensory and emotional needs that may be driving stimming behaviors.
It’s important to note that stimming behaviors are not necessarily harmful or disruptive, and may be a natural and healthy way for individuals with ASD to cope with their environment. If stimming behaviors are causing distress or interfering with daily functioning, it may be helpful to seek the advice of a healthcare professional.
Toe walking or tip-toeing is a gait pattern where a person walks on the balls of their feet without their heels touching the ground. This behavior is relatively common in young children who are learning to walk and typically resolves on its own. However, in some cases, toe walking can persist into later childhood and be associated with other conditions such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
Toe walking can be a sign of sensory issues in individuals with ASD, and it may also be a way of self-stimulation or self-regulation. In some cases, it may also be a result of muscle tightness or weakness, neurological conditions, or structural abnormalities in the legs and feet.
If your child with ASD is toe walking, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Treatment may involve physical therapy to address any muscle or joint issues, as well as sensory integration therapy to help the child learn to process and respond to sensory information more effectively. Additionally, behavioral therapy can help children learn alternative ways to self-regulate, such as deep breathing or using a fidget toy. In some cases, braces or orthotics may be recommended to help correct the gait pattern.
It’s important to note that not all individuals with ASD who toe walk require treatment, especially if the behavior does not cause any functional impairments or discomfort
WHAT IS ELOPEMENT?
 The autism community uses many terms to describe the fact that children and dependent adults with ASD depart safe spaces to put themselves in harm’s way. A mother might say her son “is a runner” or that he “bolts” when they are in public places. A father might say his daughter “wanders” or “elopes.” It’s difficult to name the behavior because we know so little about it. Is it aimless, or are these individuals trying to reach a place or person? Is it motivated by fear, sensory-sensitivity, boredom, or curiosity?
The autism community uses many terms to describe the fact that children and dependent adults with ASD depart safe spaces to put themselves in harm’s way. A mother might say her son “is a runner” or that he “bolts” when they are in public places. A father might say his daughter “wanders” or “elopes.” It’s difficult to name the behavior because we know so little about it. Is it aimless, or are these individuals trying to reach a place or person? Is it motivated by fear, sensory-sensitivity, boredom, or curiosity?
The following tips will help to ensure your child’s safety.
1. Educate all team members. If your child works with a team at school, private therapists in your home or a therapy office, or any other setting, it is important that you share with them that your child has a tendency to elope. This will help the team to keep an extra eye on your child when in their care.
2. Get an ID tag/necklace/bracelet. Regardless of whether you choose a tag tied to your child’s shoelace, a bracelet or a necklace, your child needs to wear some form of identification. If they do wander and they are nonverbal, this will be the most efficient way for first responders and/or others to know your child has autism, may be nonverbal and have your contact information to connect you back to your child as soon as possible.
3. Teach your child who is “safe.” It is important to teach your child that first responders (e.g., firefighters, cops, other medical responders) are safe and helpful people. You can do this by showing your child pictures of first responders and letting your child know, these people are your friends, they help us.
4. Enroll your child in swim classes. There are classes available for children with autism. Google around and see if you can find any in your area. It Is not only important to teach your child to learn to swim (to prevent water deaths, which we hear about too often in the news) but it’s important to teach your child to swim with their clothes on. It will take a specialized swim teacher to successfully do this with your child so don’t just stick them in a swim class with anybody!
5. Invest in more locks! It is important to secure your home and add extra locks that your child cannot reach or does not have a key to unlock to the main doors in and out of your home. The only way you will be able to use the bathroom in peace, free of worry, is if you secure your home properly. Alarm systems are also another great way to do this, so you are alerted each time someone opens or closes the doors to your home.
Over time your child can be taught that it is not safe to leave the house without mom, dad or another caregiver present. But chances are this will be a challenge to teach your child and even when you are up for that challenge, it takes time. Take action now and put a plan in place to keep that child you love so much safe. Using the tips provided today will help put you on the right track to protecting your child from wandering.
Language
 Echolalia is a repetitive speech behavior characterized by the repetition of words or phrases spoken by another person. It is often seen in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), but it can also occur in other developmental and neurological conditions.
Echolalia is a repetitive speech behavior characterized by the repetition of words or phrases spoken by another person. It is often seen in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), but it can also occur in other developmental and neurological conditions.
There are two types of echolalia: immediate echolalia and delayed echolalia. Immediate echolalia involves the immediate repetition of words or phrases heard, while delayed echolalia involves the repetition of words or phrases heard previously, sometimes days or weeks earlier.
Echolalia can serve different purposes for individuals with ASD, such as communication, self-stimulation, or a way of processing language. It can also be a way for individuals with ASD to express their desires, needs, and emotions.
While echolalia can be a normal part of language development in young children, persistent and excessive echolalia can interfere with communication and social interaction. Speech and language therapy can help individuals with echolalia to develop more functional language skills and reduce the frequency and intensity of echolalia.
Nonverbal communication difficulties are common among individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This means that they may struggle to understand and use nonverbal cues such as eye contact, facial expressions, gestures, and tone of voice. This can make it challenging for them to interact with others, understand social situations, and express their own thoughts and feelings effectively.
For individuals with ASD who are nonverbal or have limited speech, alternative communication methods such as sign language, picture exchange communication systems (PECS), and augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices may be helpful. These tools can allow individuals to communicate their wants and needs, express their feelings, and interact with others more effectively.
In addition to alternative communication methods, behavioral therapy such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) and speech therapy can be effective in improving communication skills in individuals with ASD. ABA therapy can help individuals learn new communication skills and improve social interaction, while speech therapy can help improve speech production and language comprehension.
It’s important to work with healthcare professionals who specialize in treating ASD to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets the unique needs of the individual. With early intervention and appropriate support, individuals with ASD can develop their communication skills and improve their quality of life.
Sensory Difficulties
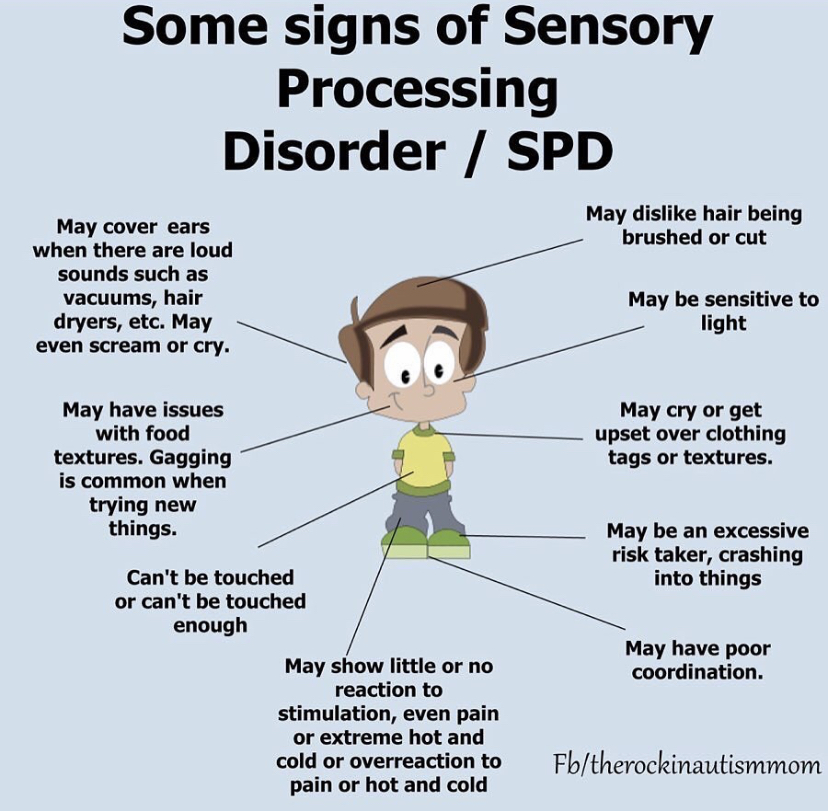 Sensory difficulties are common among individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This means that they may have differences in the way they perceive and process sensory information from their environment, such as sounds, sights, textures, tastes, and smells. These sensory differences can affect how they interact with their environment, communicate with others, and respond to social situations.
Sensory difficulties are common among individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This means that they may have differences in the way they perceive and process sensory information from their environment, such as sounds, sights, textures, tastes, and smells. These sensory differences can affect how they interact with their environment, communicate with others, and respond to social situations.
Some individuals with ASD may be hypersensitive to sensory stimuli, which means that they may feel overwhelmed or overstimulated by certain sounds, lights, or textures. Others may be hyposensitive, which means that they may not be as responsive to sensory stimuli as typical individuals. For example, they may not respond to pain or may seek out intense sensory experiences such as spinning or jumping.
Occupational therapy (OT) is a common treatment approach for sensory difficulties in individuals with ASD. OT can help individuals learn how to regulate their responses to sensory stimuli, develop coping strategies, and improve their sensory processing skills. Sensory integration therapy is a type of OT that focuses on helping individuals integrate and process sensory information more effectively.
In addition to occupational therapy, environmental modifications can also be helpful for individuals with ASD. This may include reducing the amount of sensory input in their environment by using noise-canceling headphones, reducing visual clutter, or providing a designated quiet space.
It’s important to work with healthcare professionals who specialize in treating ASD to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets the unique needs of the individual. With appropriate support and interventions, individuals with ASD can learn to manage their sensory difficulties and improve their overall quality of life
High Functioning Autism
High Functioning Autism (HFA) is a term used to describe individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) who have average or above-average intelligence and good verbal skills, but still experience challenges with social interaction, communication, and sensory processing. HFA is not a medical diagnosis, but rather a descriptive term used to differentiate individuals with ASD who have good cognitive and language abilities from those who have intellectual disability or language impairment.
Individuals with HFA may have difficulty with nonverbal communication, such as making eye contact, interpreting facial expressions, and understanding social cues. They may also have difficulty with social interaction, such as making friends or participating in group activities. Additionally, they may experience sensory processing difficulties, such as being sensitive to certain sounds, textures, or smells.
Treatment for HFA typically involves a combination of behavioral therapy, medication, and support from parents, educators, and therapists. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and social skills training can be effective in helping individuals with HFA to learn appropriate social skills and communication strategies. Medications such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications may also be used in some cases to manage symptoms of anxiety or depression.
It’s important to note that every individual with HFA is unique and may experience different challenges and strengths. With early diagnosis and appropriate interventions, individuals with HFA can learn to cope with their symptoms, build social skills, and lead fulfilling lives.




